
Pre-auricular sinus/pit: a common congenital deformity that appears as a dimple in the pre-auricular region.Inspect the pre-auricular region (in front of the ear): Scars: indicative of previous surgery (e.g.Erythema and swelling: typically associated with mastoiditis.
#Weber test skin#
basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma) skin changes.


Ask the patient if they can now hear the sound again. Confirm the patient can hear the sound of the tuning fork and then ask them to tell you when they can no longer hear it.ģ. When the patient can no longer hear the sound, move the tuning fork in front of the external auditory meatus to test air conduction.Ĥ. Place a vibrating 512 Hz tuning fork firmly on the mastoid process (apply pressure to the opposite side of the head to make sure the contact is firm). Tap a 512Hz tuning fork and place in the midline of the foreheadġ. Here the thresholds are 34db for a whisper and 56db for a conversational voice. If there is no response use a conversational voice (48db or worse) or loud voice (76db or worse).Ĥ. If there is no response you can move closer and repeat the test at 15cm. If they get two-thirds or more correct then their hearing level is 12db or better. If possible shield the patient’s eyes to prevent any visual stimulus.ģ. Ask the patient to repeat the number or word back to you. Mask the ear not being tested by rubbing the tragus. Do not place your arm across the face of the patient when rubbing the tragus, it is far nicer to occlude the ear from behind the head.
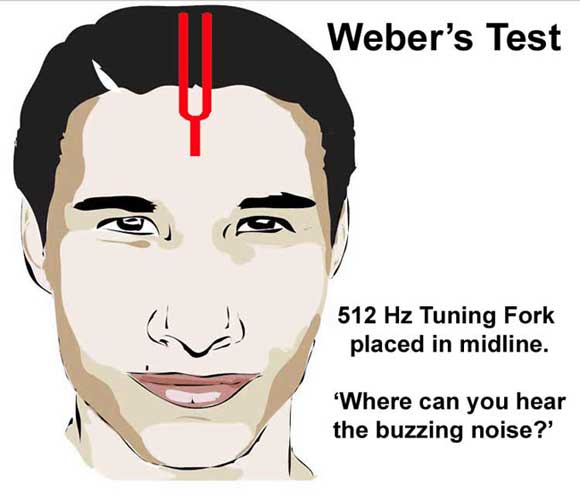
Position yourself approximately 60cm from the patient’s ear and then whisper a number or word.Ģ. The patient may have vestibulocochlear nerve pathology causing both hearing and balance issues.Īsk the patient if they have noticed any change in their hearing recently.Įxplain that you’re going to say 3 words or 3 numbers and you’d like the patient to repeat them back to you (choose two-syllable words or bi-digit numbers). Mobility aids: items such as wheelchairs and walking aids give an indication of the patient’s current mobility status.Hearing aids: note if the patient is wearing a hearing aid and ask the patient to remove this when performing otoscopy.Look for objects or equipment on or around the patient that may provide useful insights into their medical history and current clinical status: You might also be interested in our OSCE Flashcard Collection which contains over 2000 flashcards that cover clinical examination, procedures, communication skills and data interpretation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
