
#REACTIVITY TABLE OF ELEMENTS SERIES#
The reactivity series starts with the cesium metal which means cesium is at the top of the reactivity series or is the most reactive metal of this series. So, the reactivity series also tells the outcome of single displacement reactions, which are used to extract metals from their ores. Zn (s) + CuSO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu (s) For example, zinc being more reactive than copper displaces copper from copper sulphate as shown in the below reaction

This is the reason for the displacement of less reactive metals by more reactive metals in the single displacement reactions.

The more reactive metals or high ranking metals reduces (donate electrons) the ions of less reactive metals or low ranking metals in the series. iii) Displacement reaction between metals Similarly, we can predict the reaction of other metals located above lead with acids with the help of reactivity series. For example, when Zn is located above lead in the series when reacts with sulphuric acid leads to the formation of zinc sulfate and H 2 gas. Lead including the metals located above it, form salts when react with hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid hydrogen gas is also produced. Similarly, we can predict the reaction of other metals with water with the help of reactivity series. For example, when potassium reacts with water potassium hydroxide and H 2 are produced as shown in the below chemical reaction For example, it can help you predict the outcome of reactions of metals with water, acids and with other metals as described below i) Reaction between metals and waterĬalcium including the metals that are situated above it in the series react with cold water to form the corresponding metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The reactivity series not only provides information about the properties and reactivity of metals but also offers various other applications. The metals that are located above the hydrogen can displace it from acids such as HCl and H 2SO 4. This is because hydrogen helps compare the reactivity of metals. Metals placed high in the series need more energy for their separation from ores and other compounds.Īlthough hydrogen is a non-metal, it is placed in the reactivity series of metals.
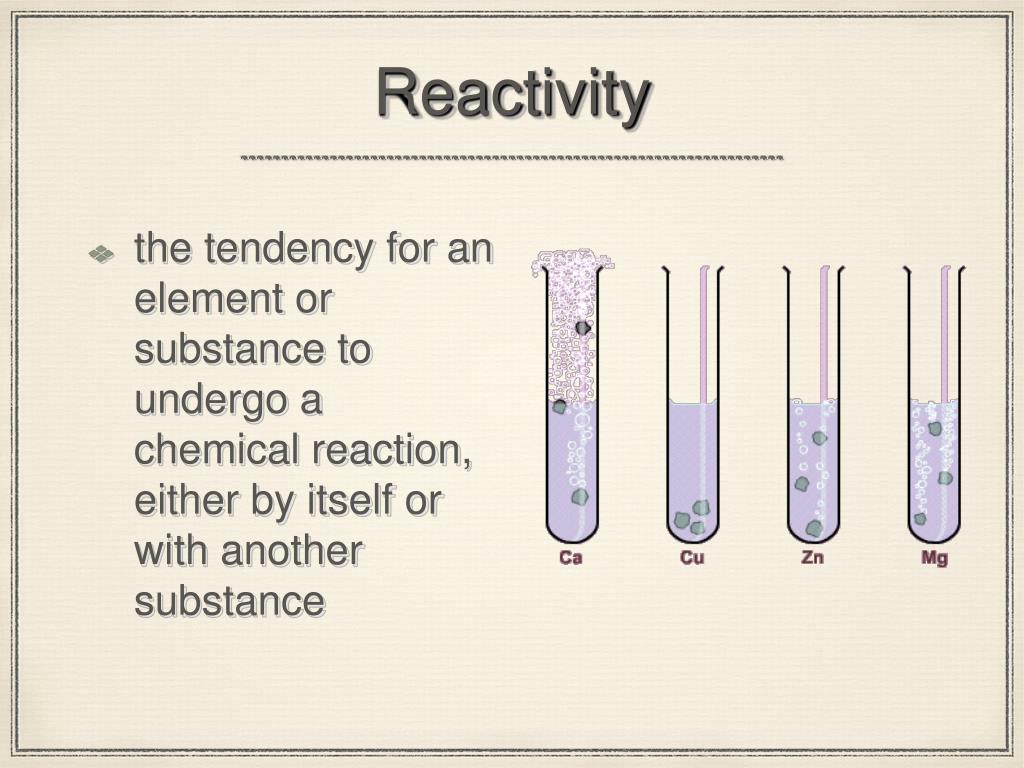
The metals at the top of this series are powerful reducing agents as they tend to lose electrons (oxidised) easily.So, it also tells about the reactivity of metals towards water and acids. The reactivity of metals is generally determined by their ability to displace hydrogen gas from water and acids. The more reactive metal tends to displace less reactive metal in displacement reactions. The reactivity series tells whether a metal can displace another metal in a displacement reaction or not. It is generally a vertically presented series that contains the most-reactive elements at the top of the series and the least-reactive elements at the bottom. So, it is a list of metals arranged in order of decreasing reactivity. It means the more reactive metals come first in this series followed by less reactive metals. In this series, the metals are arranged in descending order of their reactivity. It refers to the reactivity series of metals or elements which are metals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
